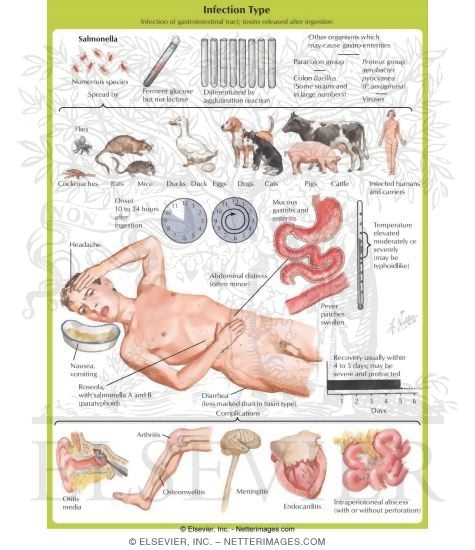
11."Food Poisoning"
-An acute, often severe gastrointestinal disorder characterized by vomiting and diarrhea and caused by eating food contaminated with bacteria, especially bacteria of the genus Salmonella, or the toxins they produce.Poisoning caused by ingesting substances, such as certain mushrooms, that contain natural toxins.



If Food Poisoning is suspected:
- Ask the patient if what food he has been eaten inn the last 48 hours.Food poisoning can take sometime to show(however, toxic food poisoning tends to act more quickly).Be alert to the possibility of ;food poisoning if there is any combination of the ff.
- Strange testing food or food that has been left out in the heat.
- Several people with the same symptoms.
- Undercooked or reheated food.
Signs and Symptoms:




- Nausea and Vomiting
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Aches and pains
- Signs of shock
Symptoms of Toxic Poisoning:
- Dizziness
- Slurred Speech
- DOB
- swallowing

Food Poisoning Prevention

Safe steps in food handling, cooking, and storage are essential to avoiding food-borne illness. Bacteria cannot be seen, smelled, or tasted, which may be on any food.Follow the CDC food safety guidelines to keep contaminants away.
Safe shopping :
- Buy cold foods last during your shopping trip.Get them home fast.
- Never choose torn or leaking packages.
- Do not buy foods past their "sell-by" or expiration dates.
- Keep raw meat and poultry separate from other foods. Pregnant women should avoid foods that can carry Listeria and should discuss healthy foods during their pregnancy with their OB/GYN physician.
Safe storage of foods
- Keep it safe;refrigerate.
- Unload perishable foods first and immediately refrigerate them. Place raw meat, poultry, or fish in the coldest section of your refrigerator.
- Check the temperature of your appliances.To slow bacterial growth, the refrigerator should be at 40 F (4.44 C),the freezer at 0 F (-17.7 C).
- Cook or freeze fresh poultry, fish, ground meats, and variety meats within two days.
Safe food preparation:
- Keep everything clean!
- Wash hands before and after handling raw meat and poultry.
- Sanitize cutting boards often in a solution of one teaspoon chlorine bleach in one quart of water.
- Do not cross-contaminate. Keep raw meat, poultry, fish, and their juices away from other food. After cutting raw meats, wash hands, cutting board, knife, and counter tops with hot, soapy water.
- Marinate meat and poultry in a covered dish in the refrigerator. Discard any uncooked/unused marinade.
Thawing food safely:
- Refrigerator: Allows slow, safe thawing. Make sure thawing juices do not drip on other foods.
- Cold water: For faster thawing, place food in a leak-proof plastic bag and submerge in cold tap water.
- Microwave: Cook meat and poultry immediately after microwave thawing.
Safe cooking:
- Use a meat thermometer
- Cook ground meats to 160 F (71 C)
- Cook ground poultry to 165 F (74 C)
- Cook beef, veal, and lamb steaks, roasts and chops to 145 F (63 C)
- Cook all cuts of fresh pork, 160 F (71 C).
- Whole poultry should reach 180 F (82 C) in the thigh; breasts 170 F (76.6 C).
- Keep hot foods hot and cold foods cold.
- Never leave food out more than two hours (or more than one hour in temperatures above 90 F [32 C]).
- Bacteria that cause food poisoning grow rapidly at room temperature.
- Use cooked leftovers within four days.

Causes:



Treatment:
- .Monitor and maintain the persons airway and breathing.If there are breathing difficulties, call 911.
- .Help the person into a comfortable position.
- Call for medical advice for medical and care.
- Give plenty of fluids to drink, particularly if the person has vomiting and diarrhea.
- Support the person if he/she vomits,providing a bowl and towel as necessary.























